每次脱节的时候,相机进行旋转
创建bool标识,在火箭脱落到最后一节,摄像机停止跟随
创建相机脚本,定义跟随对象,偏移量
更新位置的代码,写在LateUpdate()中,否则会有抖动的效果
每次跟新目标点方法
tween杀死动画的api .Kill
火箭头变短方法,主要通过改变Z轴
重新创建Transform[],
当前索引必须小于数组Length-1,否则return;
当索引等于数组长度,代表最后一节已经脱落
火箭脱落一节,速度对应增加1
创建火箭部分脱落方法,Update中鼠标左键按下调用
思路:脱离父对象,作为单独一个部分,不随着火箭整体移动
定义transform[]类型的数组
Time.time 运行程序即开始ji'shi
创建玩家数据管理类,UI管理类,音频管理类
矩阵的简单介绍
矩阵分 行 和 列
例如:
3 X 4 阶矩阵
3 是 行
4 是 列
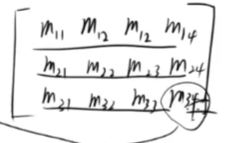
不错!
// Stretch a mesh at an arbitrary angle around the X axis.
// Angle and amount of stretching.
public float rotAngle;
public float stretch;
MeshFilter mf;
Vector3[] origVerts;
Vector3[] newVerts;
void Start()
{
// Get the Mesh Filter component, save its original vertices
// and make a new vertex array for processing.
mf = GetComponent< MeshFilter > ();
origVerts = mf.mesh.vertices;
newVerts = new Vector3[origVerts.Length];
}
void Update()
{
// Create a rotation matrix from a Quaternion.
Quaternion rot = Quaternion.Euler(rotAngle, 0, 0);
Matrix4x4 m = Matrix4x4.TRS(Vector3.zero, rot, Vector3.one);
// Get the inverse of the matrix (ie, to undo the rotation).
Matrix4x4 inv = m.inverse;
// For each vertex...
for (var i = 0; i < origVerts.Length; i++)
{
// Rotate the vertex and scale it along its new Y axis.
var pt = m.MultiplyPoint3x4(origVerts[i]);
pt.y *= stretch;
// Return the vertex to its original rotation (but with the
// scaling still applied).
newVerts[i] = inv.MultiplyPoint3x4(pt);
}
// Copy the transformed vertices back to the mesh.
mf.mesh.vertices = newVerts;
}
沿着x轴反向旋转,然后y方向拉伸,然后再旋转回来
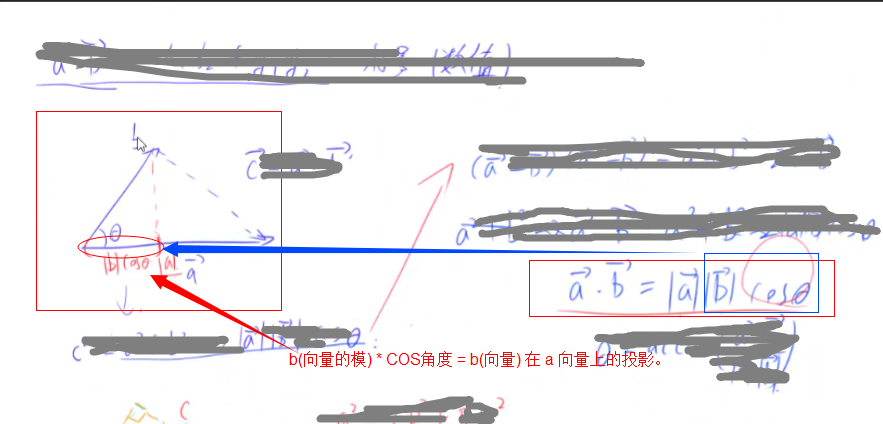
向量点乘
向量点乘的几何意义
a(向量) * b(向量) > 0
向量夹角 < 90° cos 为 正 [ -90 , 90 ]
a(向量) * b(向量) = 0
向量垂直 cos 为 0 ( -90 , 90 ,270 ,... )
a(向量) * b(向量) < 0
向量夹角 > 90° cos 为 负 [ -90 , -270 ]
向量的点乘 有 2 个公式
( 这2个公式求得的最后结果都是一样的,一个标量 )
公式1:
OA(向量) * OB(向量) = ( x1 * x2 ) + ( y1 * y2 )
公式2:
OA(向量) * OB(向量) = OA(向量的模) * OB(向量的模) * COS(向量夹角)
(1、灵活运用这2个公式可以求的俩个向量的点乘
2、也可以求的俩个向量的夹角
3、一个向量在另一个向量上的投影。)
俩个向量之间的点乘相当于,A 向量在 B 向量上的投影 * B 向量的模长
三维向量叉乘
I a(向量) x b(向量) I = I a(向量) I I b(向量) I sin角度
叉乘得到的最终向量的方面,按照所遵循的左手和右手定则 而不同。
叉乘的意义:
判断三角面的朝向。
叉乘的值
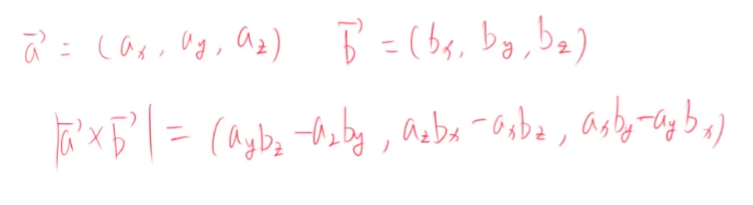
#### 叉积的应用
* 得到一个平面的法向量
* 判断旋转方向:axb旋转方向就是从a到b,顺时针和逆时针取决于观察方向,走到对侧观察,顺逆性就刚好反过来了。
** 用左手定则,假设知道了axb(中指),和a(大拇指),我们大致可以判断b的方向,知道axb(大拇指)和b(食指)也是一样。在该系中,axb,a到b永远是顺时针。 +
就是说,站在大拇指和食指形成的平面,头朝向axb观察,是顺时针,顺时针就是角度变大的旋转方向。
** 0 共线(可能同向,或反向)
### unity中的点和向量
vector2 vector3 分别用来表示二维 或 三维 的点或向量。
* transform.position transform所在对象在世界坐标系中的点的位置
* transform.forwoard 等相关值,是transform所在对象z正向在世界坐标系的单位向量
* 在unity中,用vector3来表示对象的位置
* 在unity中,*用vector3来表示物体移动的长度和方向*。
** update函数相当于差分,每帧移动ds距离
** 设匀速运动s=vt,则ds=v*dt,从t到t+1秒积分得:s=v,也就是说,累积一秒的若干帧更新,刚好走过了速度标定的距离,因此我们也把向量当作速度来用
*** update函数中的移动距离计算为:ds=time.deltatime*移动矢量,其中移动矢量是一秒物体移动的距离,也就是速度
* 在unity中,可以通过两个对象transform.position值相减得到的矢量的模,得到两个对象的距离
[source,csharp]
----
private Vector3 movingvect;
private bool movingSetted=false;
private float movingtime=3;
//set in inspector panel
public Transform target;
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
//第一次,求移动矢量,也就是距离
if (movingSetted==false){
movingSetted=true;
movingvect=target.position-transform.position;
}
//距离足够小停止运动
var distanceVector=target.position-transform.position;
//模平方获得较好运行性能
if(Vector3.SqrMagnitude(distanceVector)>=0.1f)
transform.Translate(movingvect/movingtime*Time.deltaTime,Space.World);
}
----
void Update()
{
//每秒移动两秒抵达屏幕边界时停止
var vpp = Camera.main.WorldToViewportPoint(transform.position);
if (vpp.x > 0 && vpp.y > 0 && vpp.x < 1 && vpp.y < 1)
transform.Translate(Time.deltaTime * Vector3.right * 2, Space.World);
}
### 屏幕坐标与视口坐标转换
#### Camera.ScreenToViewportPoint
public Vector3 ScreenToViewportPoint(Vector3 position);
Transforms position from screen space into viewport space.
Screenspace is defined in pixels. The bottom-left of the screen is (0,0); the right-top is (pixelWidth,pixelHeight). The z position is in world units from the camera.
#### Camera.ViewportToScreenPoint
public Vector3 ViewportToScreenPoint(Vector3 position);
Transforms position from viewport space into screen space.
Viewport space is normalized and relative to the camera. The bottom-left of the camera is (0,0); the top-right is (1,1). The z position is in world units from the camera.
//下列两条语句等价
transform.Translate(Time.deltaTime*transform.up,Space.World);
transform.Translate(Time.deltaTime*Vector3.up);
## 坐标系关联与相互转换
### Transform.Translate
`public void Translate(Vector3 translation, Space relativeTo = Space.Self);`
将transform,相对于space坐标系,移动translation的距离
* 移动谁:移动transform所在对象
* 相对于哪个坐标系移动:相对于space移动
* 移动多少:移动translation
* space枚举取值有哪些:space.world,space.self(默认值)
## Transform.TransformPoint
`public Vector3 TransformPoint(Vector3 position);`
将本transform空间中的点position,转换到世界坐标系。
## Transform.InverseTransformPoint
`public Vector3 InverseTransformPoint(Vector3 position);`
将世界坐标系中的点position,转换到本transform的局部坐标系



